Quickstart: Launch Workloads with GPU Fractions¶
Introduction¶
Run:ai provides a Fractional GPU sharing system for containerized workloads on Kubernetes. The system supports workloads running CUDA programs and is especially suited for lightweight AI tasks such as inference and model building. The fractional GPU system transparently gives data science and AI engineering teams the ability to run multiple workloads simultaneously on a single GPU, enabling companies to run more workloads such as computer vision, voice recognition and natural language processing on the same hardware, lowering costs.
Run:ai’s fractional GPU system effectively creates logical GPUs, with their own memory and computing space that containers can use and access as if they were self-contained processors. This enables several workloads to run in containers side-by-side on the same GPU without interfering with each other. The solution is transparent, simple, and portable; it requires no changes to the containers themselves.
A typical use-case could see a couple of Workloads running on the same GPU, meaning you could multiply the work with the same hardware.
The purpose of this article is to provide a quick ramp-up to running a training Workload with fractions of a GPU.
There are various ways to submit a Workload:
- Run:ai command-line interface (CLI)
- Run:ai user interface
- Run:ai API
Prerequisites¶
To complete this Quickstart, the Platform Administrator will need to provide you with:
- Researcher access to Run:ai
- To a Project named "team-a"
- With at least 1 GPU assigned to the project.
- A link to the Run:ai Console. E.g. https://acme.run.ai.
- To complete this Quickstart via the CLI, you will need to have the Run:ai CLI installed on your machine. There are two available CLI variants:
Step by Step Walkthrough¶
Login¶
Run runai login and enter your credentials.
Run runai login and enter your credentials.
Browse to the provided Run:ai user interface and log in with your credentials.
To use the API, you will need to obtain a token. Please follow the api authentication article.
Run Workload¶
Open a terminal and run:
- In the Run:ai UI select Workloads
- Select New Workload and then Training
- You should already have
Cluster,Projectand astart from scratchTemplateselected. Enterfrac05as the name and press CONTINUE. - Select NEW ENVIRONMENT. Enter
quickstartas the name andrunai.jfrog.io/demo/quickstartas the image. Then select CREATE ENVIRONMENT. - When the previous screen comes up, select
half-gpuunder the Compute resource. - Select CREATE TRAINING.
- Follow the process again to submit a second workload called
frac05-2.
Note
For more information on submitting Workloads and creating Assets via the user interface, see Workload documentation.
curl -L 'https://<COMPANY-URL>/api/v1/workloads/trainings' \ # (1)
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer <TOKEN>' \ # (2)
-d '{
"name": "frac05",
"projectId": "<PROJECT-ID>", '\ # (3)
"clusterId": "<CLUSTER-UUID>", \ # (4)
"spec": {
"image": "runai.jfrog.io/demo/quickstart",
"compute": {
"gpuRequestType": "portion",
"gpuPortionRequest" : 0.5
}
}
}'
<COMPANY-URL>is the link to the Run:ai user interface. For exampleacme.run.ai<TOKEN>is an API access token. see above on how to obtain a valid token.<PROJECT-ID>is the the ID of theteam-aProject. You can get the Project ID via the Get Projects API<CLUSTER-UUID>is the unique identifier of the Cluster. You can get the Cluster UUID by adding the "Cluster ID" column to the Clusters view.
Note
- The above API snippet will only work with Run:ai clusters of 2.18 and above. For older clusters, use, the now deprecated Cluster API.
- For more information on the Training Submit API see API Documentation
- The Workloads are based on a sample docker image
runai.jfrog.io/demo/quickstartthe image contains a startup script that runs a deep learning TensorFlow-based workload. - We named the Workloads frac05 and frac05-2 respectively.
- The Workloads are assigned to team-a with an allocation of half a GPU.
List Workloads¶
Follow up on the Workload's progress by running:
The result:
The result:
Showing jobs for project team-a
NAME STATUS AGE NODE IMAGE TYPE PROJECT USER GPUs Allocated (Requested) PODs Running (Pending) SERVICE URL(S)
frac05 Running 9s runai-cluster-worker runai.jfrog.io/demo/quickstart Train team-a yaron 0.50 (0.50) 1 (0)
frac05-2 Running 8s runai-cluster-worker runai.jfrog.io/demo/quickstart Train team-a yaron 0.50 (0.50) 1 (0)
- Open the Run:ai user interface.
- Under
Workloadsyou can view the two new Training Workloads
View Partial GPU memory¶
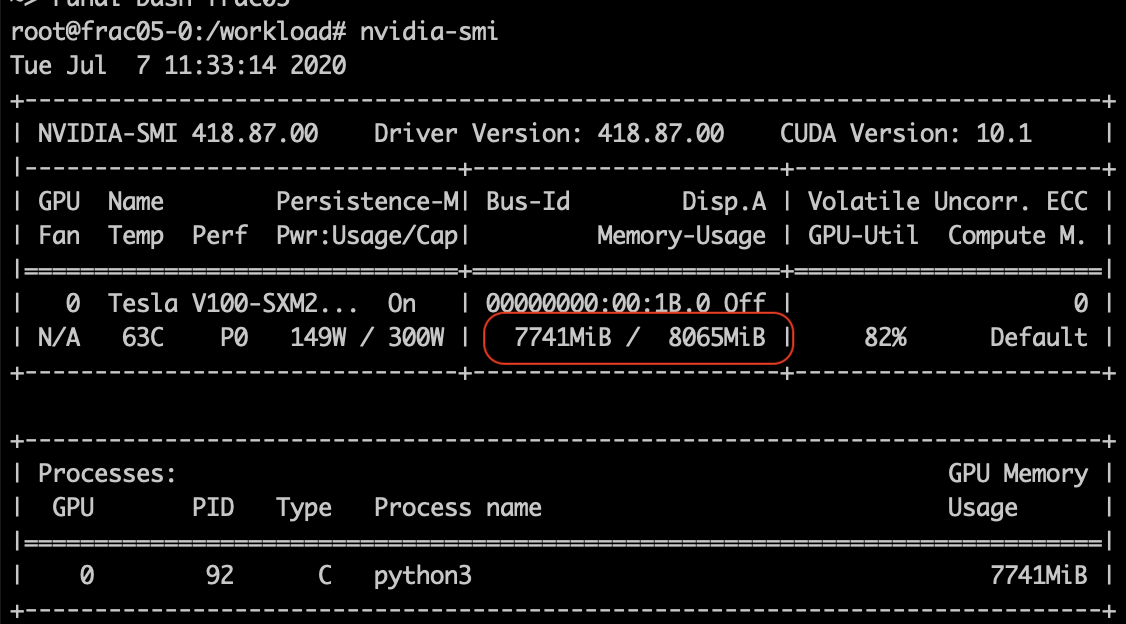
To verify that the Workload sees only parts of the GPU memory run:
The result:
Notes:
- The total memory is circled in red. It should be 50% of the GPUs memory size. In the picture above we see 8GB which is half of the 16GB of Tesla V100 GPUs.
- The script running on the container is limited by 8GB. In this case, TensorFlow, which tends to allocate almost all of the GPU memory has allocated 7.7GB RAM (and not close to 16 GB). Overallocation beyond 8GB will lead to an out-of-memory exception
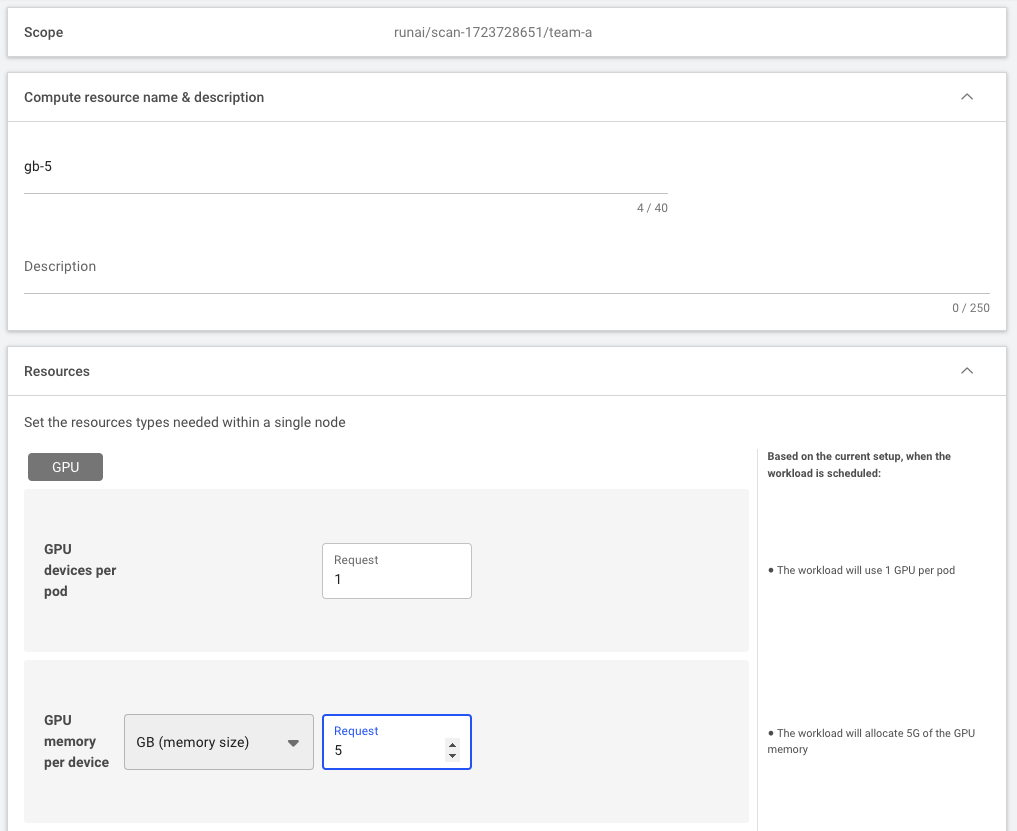
Use Exact GPU Memory¶
Instead of requesting a fraction of the GPU, you can ask for specific GPU memory requirements. For example:
Which will provide 5GB of GPU memory.